
It is imminent to find replacements for second- and third-generation refrigerants!
On September 15, 2021, the "Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer" entered into force for China. According to the "Montreal Protocol", the second-generation refrigerant HCFC will cease to be used in 2030. The amendment requires that by 2050, global HFCs consumption will drop by about 85%.
This is a milestone event in the refrigerant phase-out process, and it also sends out a huge political signal that the international community is determined to phase out the use of HFCs.
At the same time, with the establishment of the domestic "dual-carbon" target and the gradual implementation of the third-generation refrigerant HFCs control policy, it is urgent to study HCFC, HFCs substitute substances and related technologies.
The refrigerant enters the era of low GWP value, and the flammability problem cannot be ignored!
Generally speaking, the use of flammable refrigerants with low GWP values to replace HCFC and other fluorine-containing gases is considered an effective and lower cost solution. However, studies have shown that traditional refrigerants rarely meet all the requirements of future refrigerants for low GWP, safety, thermodynamic performance and environmental performance at the same time.
In other words, many low GWP values are combustible!
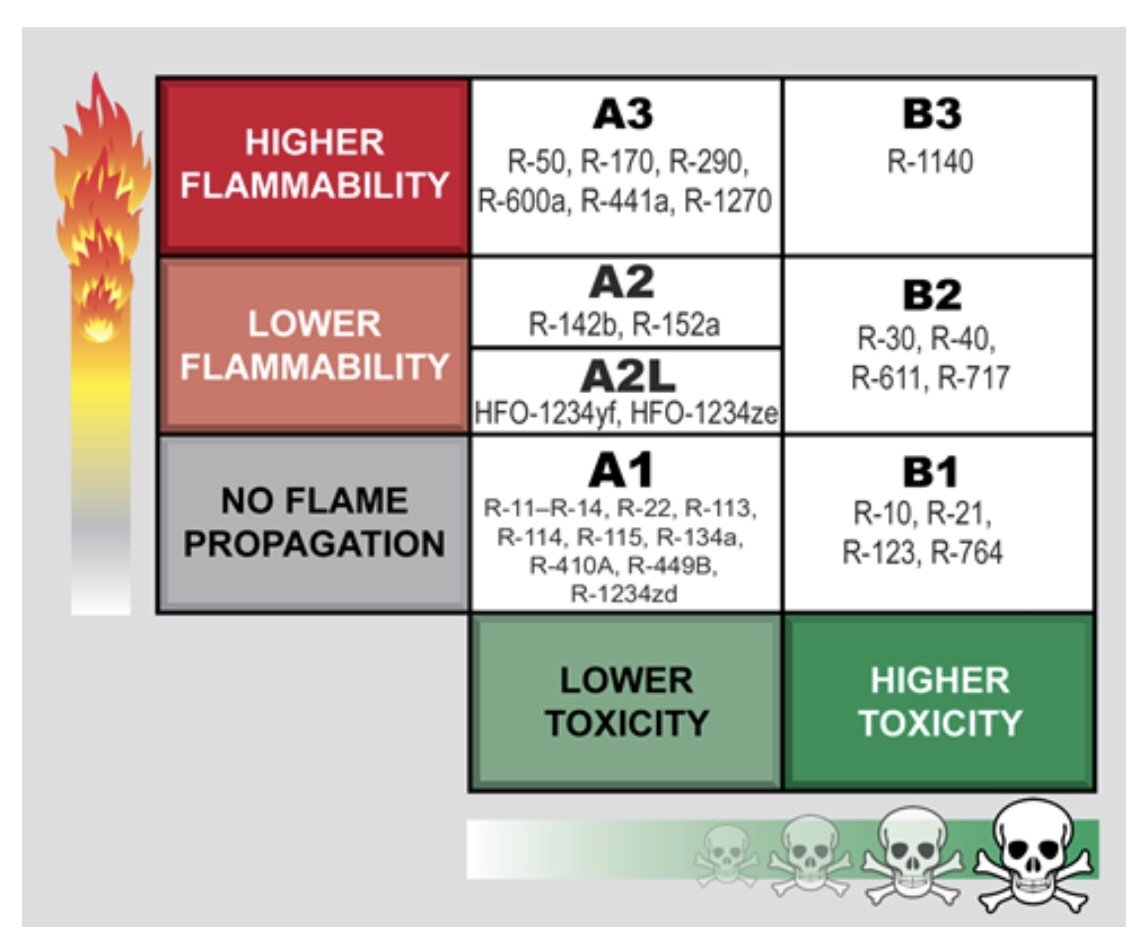
The national standard "Refrigerant Numbering Method and Safety Classification" GB/T 7778-2017 divides the toxicity of refrigerants into Class A (low chronic toxicity) and Class B (high chronic toxicity), and flammability is classified into Class 1 ( No flame propagation), Class 2L (weakly possible), Class 2 (feasible), and Class 3 (flammable and explosive). According to GB/T 7778-2017, the safety of refrigerants is subdivided into 8 categories, namely: A1, A2L, A2, A3, B1, B2L, B2, and B3. Among them, A1 is the safest and B3 is the most dangerous.
How to use A2L HFO refrigerant safely and efficiently?
Although household air conditioners, central air conditioners and other refrigeration equipment have been tested for performance at the factory, the reference value of the refrigerant charge is indicated. However, many large central air-conditioning units and industrial chillers need to be filled with refrigerant on-site, as do household air-conditioners, refrigerator equipment, cold storage, etc. during the maintenance process.
Moreover, because of the different types of evaporators used in some equipment, the refrigerant charge is different. In addition to the maintenance and installation site, due to the limited conditions, many maintenance workers charge refrigerant based on experience. In addition, the industry is also very sensitive to the issue of refrigerant flammability.
Based on this, Chemours has launched R1234yf, R454A, R454B, R454C and other weakly flammable A2L, low GWP refrigerants, and is committed to promoting system design and popular science training to solve flammability risks.
The A2L safety level has the attributes of low toxicity (A) and weak flammability (2L). Many A2L HFO refrigerants have both high performance and low GWP characteristics, and are ideal substitutes for the previous generation of HFC refrigerants. A2L products are not only widely used in the international market, but many domestic companies have also accelerated the pace of upgrading and introducing this new type of refrigerant into production applications. For example, Johnson Controls uses Oteon™ XL41 (R-454B) in its York ® YLAA scroll chiller for the European market; Carrier also chooses R-454B (that is As its main low-GWP refrigerant, Carrier will use R-454B in its tubular residential and light commercial HVAC products sold in North America from 2023. Replace R-410A.

Post time: Oct-23-2021




